Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body tissue by producing chemicals that break down the tissue and cause inflammation. This occurs particularly in the synovium- or joint lining. It often begins in smaller joints such as the fingers and toes and spreads to include other joints of the body.
Symptoms
Pain
Stiffness- especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity
Swelling and inflammation
Warmth around the joint
Deformity or contracture
Symptoms may occur in other systems of the body such as fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and weakness.
Symptoms can come and go as well as vary in severity
Causes
Environmental factors or infection activates an inherited gene- rheumatoid factor
This gene makes you more susceptible to certain environmental factors that may trigger the disease but does not necessarily “cause” the disease to present
Tendons and ligaments that hold joint together weaken and tear as they are attacked as well, causing the joint to lose its shape and alignment
Risk Factors
Women
Can occur at any age but usually presents in middle age
Smoking
Exposure to environmental triggers such as asbestos
Obesity
Prevention
Avoidance of environmental triggers
Non-smoking
Maintain a healthy weight
Diagnosis
Physician will take detailed medial history and physical exam
Lab tests to check for rheumatoid factor, anti-cyclic citrullated peptide antibodies, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or C-reactive protein
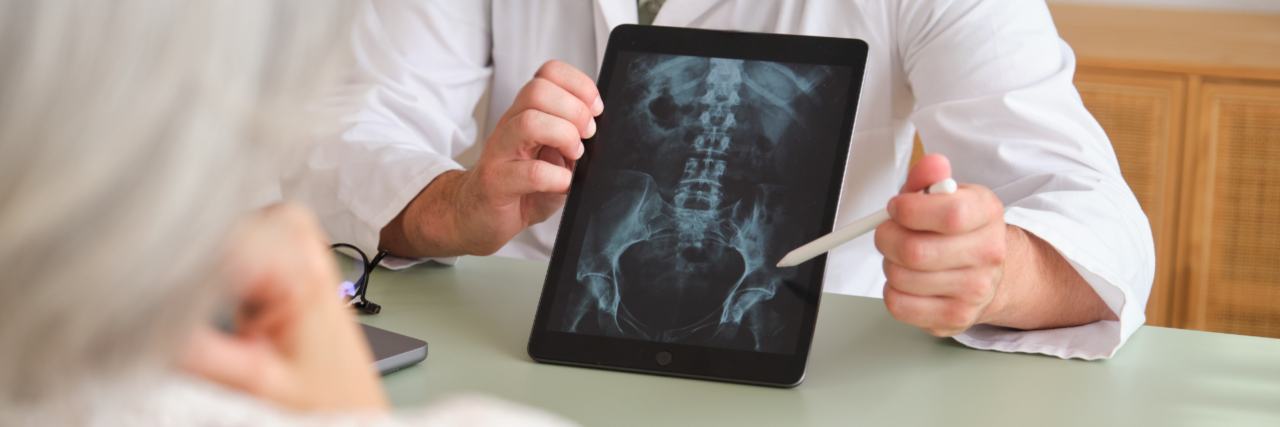
X-ray and MRI to evaluate progression of disease
Patient must have 4 of the 7 identifiable criteria:
Morning stiffness lasting an hour or more
Arthritis of 3 or more joints for 6 weeks
Arthritis of hand joints for at least 6 weeks
Arthritis on both sides of the body for at least 6 weeks
Rheumatoid nodules under the skin
Rheumatoid factor present in blood testing
Evidence of rheumatoid arthritis on x-rays
Treatment Options
Non-surgical:
Medications: type of medication depends on the severity of the disease (NSAIDS, corticosteroids, or disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs))
Physical therapy or occupational therapy to keep joints healthy
Orthotics to make everyday tasks easier and less painful
Surgical:
Synovectomy- removal of joint lining
Tendon repair- to tighten the tendons stretched or damaged
Joint fusion
Joint replacement