Patellar tendonitis is an overuse injury to the tendon just below the patella- or knee-cap.
Symptoms
- Pain between the patella and where the patellar tendon attaches to your lower leg
- Pain intensifies with activity and gradually gets worse over time
- Pain while climbing stairs or getting up from a chair
- Inflammation or swelling of tendon under patella
Causes
- Repetitive jumping and landing activity in sport
- Repeated stress on the patellar tendon which creates tiny tears that inflame and weaken the tendon over time
- Muscular imbalances in legs, especially in the thigh
- Misalignment of feet, ankles, knees, or hips
- Chronic disease that weakens the tendon over time
Risk factors
- Most common in those in 20s and 30s.
- Sports that involve frequent jumping and landing
- An athlete that is still growing
- Sudden increase in exercise duration or intensity
- Tight thigh muscles
- Chronic disease such as kidney failure, autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
- Taller and heavier athletes or obesity
- Improper shoes
Prevention
- Proper warm up and cool down
- Focus on proper technique
- Do not play through pain
- Strengthen muscles to reduce muscular imbalances
- Maintain a healthy body weight
Diagnosis
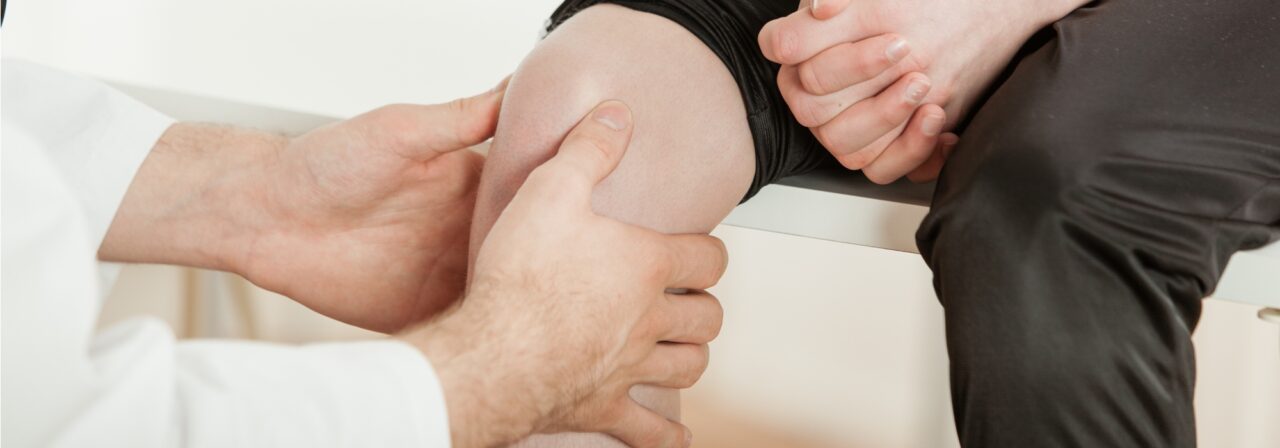
- Thorough physician exam including a history, observation, and palpation of the area that hurts
- X-rays, Ultrasound, or MRI may be ordered to narrow down diagnosis
Treatment options
Non-surgical treatment options
- Rest and avoidance of painful activity
- Ice and elevation of the area
- Regular stretching of the quadriceps and hamstring muscles
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication
- Patellar tendon strap or brace
Surgical treatment options
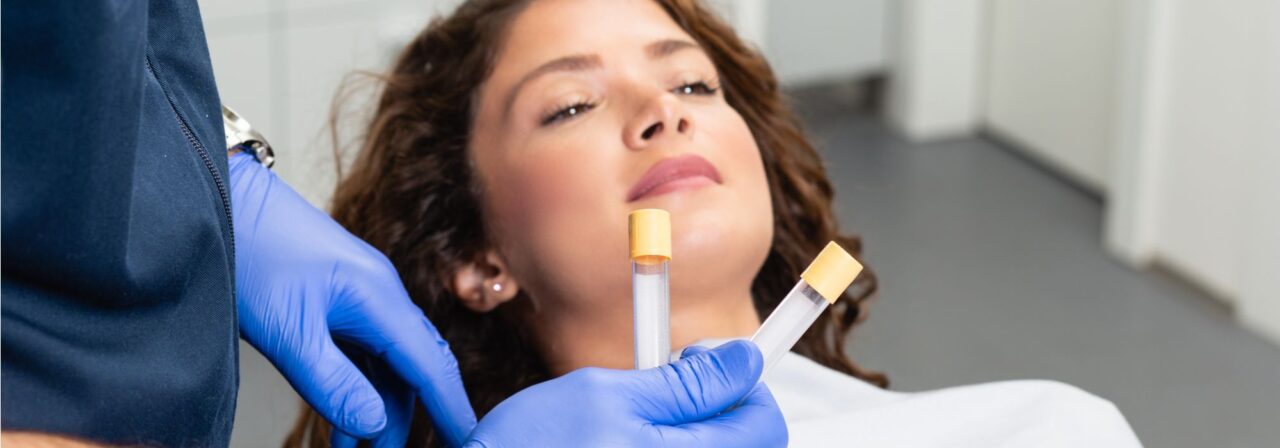
- Corticosteroid injection
- Plasma rich platelet (PRP) injection
- Surgical debridement through arthroscopy